President Donald Trump has officially signed into law the creation of a U.S. sovereign wealth fund. This is one of the few of his controversial executive orders that have been signed that may have a bit of merit when it comes to addressing the affordability crisis the United States is facing.
A sovereign wealth fund is a government investment fund that pools and manages a nation’s revenues, often derived from natural resources, trade surpluses, or foreign exchange reserves, to generate long term wealth and stabilize the economy. Several economic powerhouses have a wealth fund: Norway, Singapore, Saudi Arabia, and the United Arab Emirates (Dubai Fund) have used SWFs to diversify their economies, invest in global assets, and provide financial security for the youth. These funds have enabled these nations to achieve high levels of economic stability, global influence, & sustained growth, even during periods of global economic uncertainty, all while empowering their citizenry.

The fund with the most long term exposure and demonstrated long term practical excellence is Singapore’s Central Provident Fund.
Singapore’s Central Provident Fund (CPF) offers a noteworthy model for the US. In the 1960s, Singapore faced significant economic challenges that necessitated comprehensive reforms. When Singapore became independent the nation faced significant economic challenges. Over 70% of households lived in overcrowded conditions, with a third residing in shanty towns on the city’s outskirts, and more than half of the population was illiterate. The situation was further exacerbated by a heavy influx of immigrants prior to Singapore’s expulsion from the Malaysian political union, leading to an unemployment rate of approximately 15-20%. (Asian Development Bank).
Fast forward 50 years, and Singapore’s transformation is remarkable. The literacy rate has soared to 97.65% as of 2021. The nation consistently ranks at the top globally in educational assessments for math, science, and reading. Unemployment has plummeted to around 2%, significantly lower than the global average of approximately 6%. Additionally, about 90.7% of Singaporeans are homeowners, a stark contrast to the United States, where the homeownership rate is at approximately 50%. This extraordinary progress can be largely attributed to the determination and hard work of Singapore’s populace, as well as the Central Provident Fund. (Asian Development Bank).
The Central Provident Fund
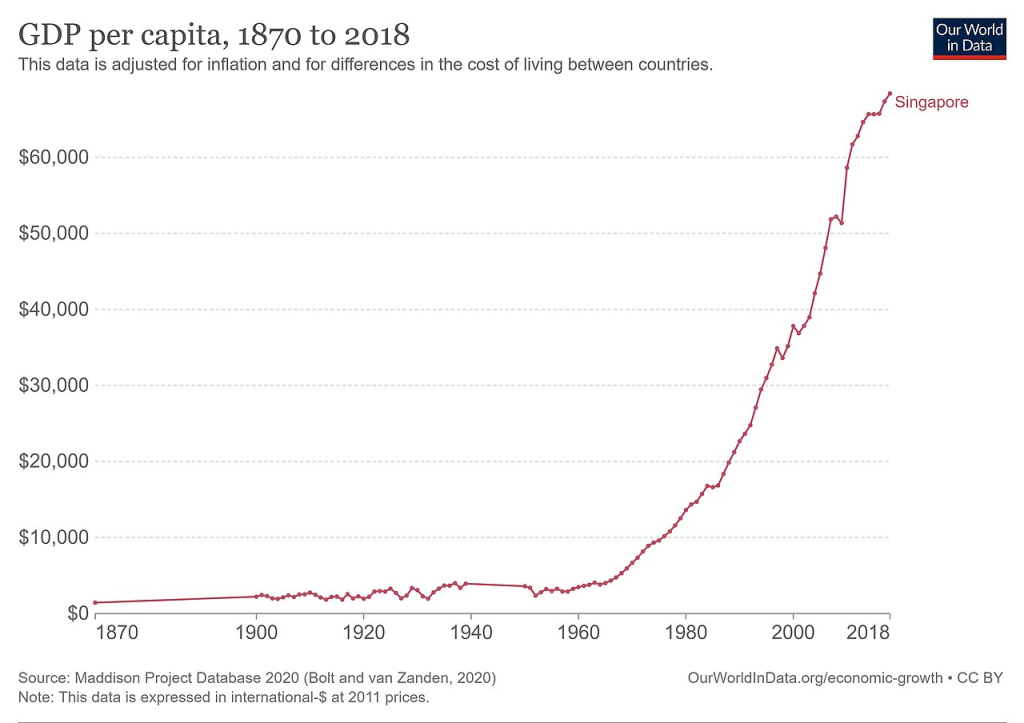
Prime Minister Lee Kuan Yew recognized the potential of the existing Central Provident Fund (CPF), established in 1955 during British colonial rule, as a tool to address economic challenges. The Fund was originally designed as a compulsory savings scheme for retirement, the CPF required contributions from both employers and employees. Unlike traditional social security systems funded by taxes, the CPF allowed individuals to own and control their savings, providing flexibility in how funds were utilized. This structure enabled citizens to manage their accounts while also engaging with private banking institutions.
In 1968, the government expanded the CPF’s scope to include housing, permitting withdrawals for the purchase of government flats. This policy not only addressed housing shortages but also fostered social stability and economic growth. Over time, the CPF’s functions further extended to cover healthcare and education, ensuring that citizens’ basic needs were met and allowing them to focus on personal development and community engagement. These strategic expansions of the CPF were instrumental in transforming Singapore’s economy and enhancing the well-being of its population (Asian Development Bank, n.d.).
After the CPF expanded its focus to housing, enabling citizens to use their savings to purchase government built housing units the homeownership rate is now up to 90% in Singapore. For the U.S., a sovereign wealth fund could potentially support housing initiatives, allowing Americans to leverage tax advantaged savings for home purchases, thereby fostering ownership and equity building. (International Monetary Fund).
Beyond housing, the CPF encompasses healthcare and education, allowing citizens to allocate savings toward medical insurance and lifelong learning. This approach reduces financial burdens and enhances productivity by alleviating concerns over essential services. A U.S. sovereign wealth fund could adopt similar strategies, offering dedicated accounts for healthcare and education expenses, possibly with employer matched contributions to accelerate wealth accumulation. (International Monetary Fund).
Implementing such a system in the U.S. presents significant challenges and hurdles . Political resistance to state managed savings programs and the complexities of federalism could impede adoption. Additionally, effective management is crucial to prevent issues like corruption or market volatility. Nevertheless, the potential benefits such as; reduced wealth inequality, increased productivity, and a buffer against economic downturns- are alluring. (PricewaterhouseCoopers).
While the executive order establishing a U.S. sovereign wealth fund is still in its early stages, Singapore’s CPF demonstrates that integrating state oversight with individual agency can transform citizens into stakeholders. For modern Americans burdened by housing costs, medical debt, and student loans, a similar fund could offer substantial relief and innovate on America’s financial institutions in a positive way.
Richard E. Carroll explores the potential for sovereign wealth funds at both the state and federal levels in the United States as a solution to financial challenges. At the state level, 20 U.S. states have established SWFs to manage natural resource revenues and benefit their citizens. For example the Alaska Permanent Fund, established in 1976, is the most well known, currently valued at over $5 billion. Many Alaskans get dividends from this fund, giving them expendable income for education or subsistence needs. New Mexico has done something similar, reducing the tax burden of the average citizen by about $1,000. I for one am a firm advocate for a SWF.
The Fund could be used to invest in infrastructure projects, such as roads, bridges, renewable energy, and broadband, creating jobs and stimulating economic growth. However, generally Americans are skeptical of government run programs, particularly those involving personal savings and investments. Therefore, building public trust would be essential for the fund’s success, perhaps including an opt out for citizens would be beneficial, but after their decision to opt out they should not be eligible to receive any benefits from the program- which is within their right. However, if the fund is managed properly, a steady stream of income from the SWF, the federal government could reduce income, corporate, or sales taxes, which could in theory put money back into the pockets of citizens and businesses. In essence America would be paying you for contributing positively to the American economy.
Having outlined all of that, the key question is whether the U.S. can adapt this model at the Federal level complicated by its diverse landscape. Time will tell.
Sources:
______________________________________________
- Asian Development Bank. (2019). Singapore’s Central Provident Fund: A model for social security. https://www.adb.org/publications/singapore-central-providend-fund
- International Monetary Fund. (2020). Sovereign wealth funds and public savings: Lessons from global models.
- PricewaterhouseCoopers. (2021). Why Sovereign Wealth Funds need to recalibrate their governance, risk and controls. https://www.pwc.com/gx/en/industries/sovereign-wealth-investment-funds/sovereign-wealth-funds-risk-recalibration.html
- Richard E. Carrol. (2023) How a United States federal sovereign wealth fund could solve the United States debt problem. https://moderndiplomacy.eu/2023/01/21/how-a-united-states-federal-sovereign-wealth-fund-could-solve-the-united-states-debt-problem/




